You may have a demo for the battery NP3 (deutsch,english,slovensky,česky) inclusive a handbook. Please contact here to order the demo.
Very brief information to every single program:
(You can obtain more detailed informastion here
|
NP3
The NP3 battery consists of 57 program modules. Each of them is described in the enclosed manual. As a rule it explains the objective of the program, i.e. what the particular task about. Its diagnostic and training value. Furthermore, it is explained how one can create further tasks for oneself or someone in the family for the program in question to be adapted to the abilities and interests of the exerciser.
The results of the actions are stored and this fact allows a good overview and monitoring of the skills concerned.
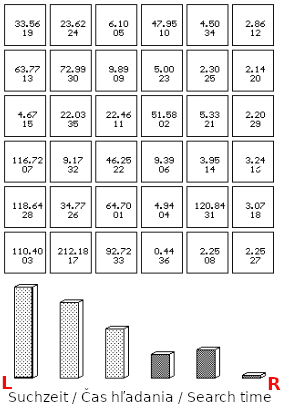
All program modules automatically provide graphical representations of the results: time, error, quantity analyses and the like.
Special program modules allow insight into the state of mind of the exerciser.
Further versions of the NP3 battery
HNP/THNP is consisting of two parts:
1./ HNP - the training program for the client
2./ THNP - the supervision programm for the supervisor
The real experience with these programs since 1999 has shown that it can be a promising path to therapy in the home environment. More information can be found by the interested reader in the free manual (PDF), which can be requested here.
The user can independently select and perform exercises. His results are stored in the local database and are available for further evaluation.
In addition, he or she or another person (family members) can - taking into account of patient-specific circumstances (interests, hobbies, profession, etc.). - create any number of new exercises.
Here are some more informationens to find.
Neglect - Disorders of the personal space
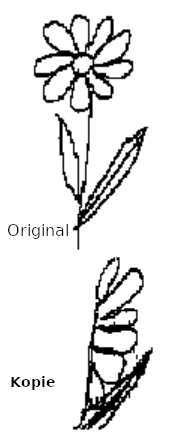 Here you can see the flower that a 42-year-old well-trained patient with so-called neglect disorder had drawn. This disorder of attention, which often occurs after a right-brain injury, is clearly noticeable in the everyday life of the injured person but the affected person is not aware of his/her deficit (= anosognosia).
Here you can see the flower that a 42-year-old well-trained patient with so-called neglect disorder had drawn. This disorder of attention, which often occurs after a right-brain injury, is clearly noticeable in the everyday life of the injured person but the affected person is not aware of his/her deficit (= anosognosia).
=========================================================================
Visuall orientation - Broken selective attention
One of the consequences of the neglect
The most obvious sign of neglect disorder is poor orientation in the space. Thus, the affected person bumps conspicuously often into obstacles on one side of the body (mostly on the left): door frames, table edges, etc. But also his reactions to being approached from the affected side are strikingly diminished.
Remember: This is NOT a disorder of vision, but one of attention.
=========================================================================
Disturbance of the ability to adequately judge the fellow human beings.
One of the consequences of the frontal brain injury
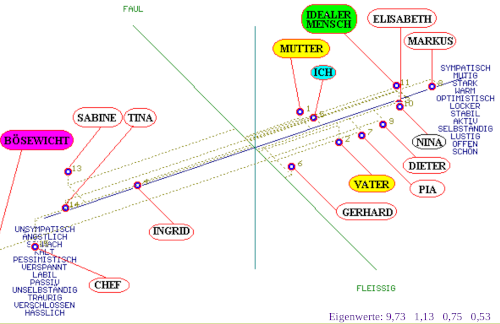
Injuries in the frontal brain lead to a series of impairments of the "higher" mental processes such as planning and action initiation, cognitive flexibility, coordination of information and processes, sequencing and goal monitoring, and many others. Researchers have shown that the reactions of the autonomic nervous system in social situations are often missing. As a result, their affective evaluations of their environment and fellow human beings flatten out. (Experimentally it could be shown that the skin resistance did not change during uncommented emotional scenes. This reaction occurred as a rule in healthy adults.)
The figure shows the factor analytic evaluation of a young woman's responses in the SEMDI (semantic differential) task. She was involved in an car accident and was unresponsive at the scene. MRI showed numerous pathological signal changes in the cerebral cortex frontal left (contusion hemorrhage left frontal), EEG : focal pathological findings both frontal sides.
The healthy subjects answer in this task in such a way that one can find by the mean of factor analysis at least 3 factors (so called E-A-P factors: evaluation-activity-potency). As can be seen in the picture, this young woman answered in a way that only one meaningful factor could be found.
=========================================================================
The most frequent deficits after TBI
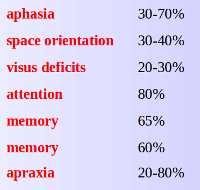
The brain injuries can lead to a number of impairments. Various authors give the following percentages of the disorders.
=========================================================================
Deficits in the ability to fill missing information
Frequent impairment in cases of traumatic brain injury or in the degenerative processes

Can you recognize what is in the picture? Are there details of the object you could describe?
=========================================================================
If you would you like to learn more about it.
go back to start